Ethical Hacking (White Hat)
Ethical Hacking
The goal of Ethical Hacking is to simulate real-world cyber threats and help organizations strengthen their defenses against potential cyberattacks. Ethical hackers employ various techniques and tools to mimic the tactics of malicious actors, providing valuable insights into a system’s vulnerabilities. By identifying and addressing these weaknesses proactively, ethical hacking plays a crucial role in enhancing overall cybersecurity, ensuring the integrity and security of digital assets while helping organizations stay one step ahead of potential cyber threats.
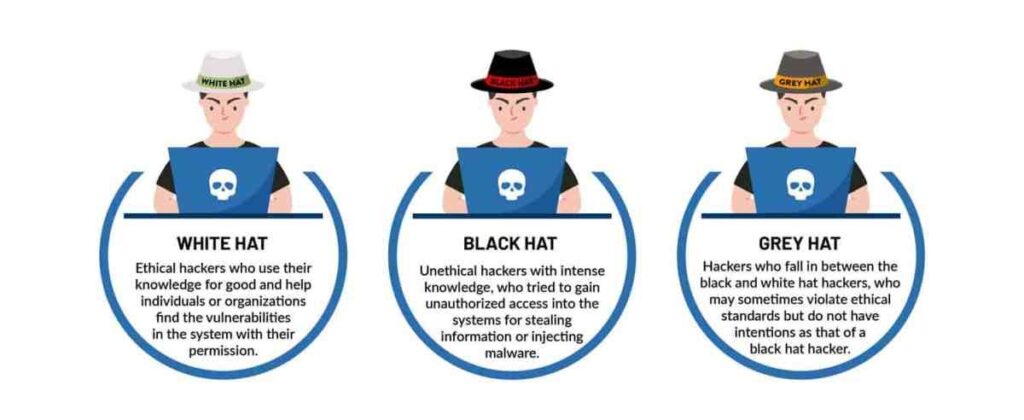
We focus on:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Ethical hackers conduct thorough assessments of systems to identify potential vulnerabilities. This involves using various tools and techniques to analyze software, network configurations, and infrastructure components.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers perform controlled simulated attacks, known as penetration tests, to exploit identified vulnerabilities. This process helps organizations understand how their systems might be compromised and allows them to address weaknesses before malicious hackers can exploit them.
- Security Auditing: Ethical hackers conduct comprehensive security audits to review and assess an organization’s overall security posture. This involves examining policies, procedures, and configurations to ensure they align with industry best practices and compliance standards.
- Social Engineering Testing: Ethical hackers often employ social engineering techniques to test the human element of security. This includes attempting to manipulate individuals within the organization to gain access or extract sensitive information, helping to uncover potential weaknesses in employee awareness and training.
- Security Patching and Remediation: Ethical hackers collaborate with organizations to develop and implement strategies for patching and remediation. After identifying vulnerabilities, they work with the IT and security teams to prioritize and address issues, ensuring that the necessary security patches and measures are applied to mitigate risks.
Starting from R1800

